In this article, I will take you through different ways to List/Get/Display/Find MAC Address in Linux. You might be aware of Ethernet Card/Network Card/NIC Controller which works at Network level and is responsible for communicating with other network devices in a Network Topology. It is used in Layer-2 Communication. You can find the usage of MAC address in wide range of Network Devices currently in use. This is typically in-line with IEEE 802 Network technologies.
Sh mac address-table interface gigabitEthernet x/x. Then on layer 3 device to resolve it to ip address take the mac from above and run. Show ip arp x.x.x. First, open Google and Type IP in search. This will display your external address. If you can browse the Internet, use the Mac command line. Launch Terminal, which is under the Utilities folder, and type: curl ifconfig.me or curl ipecho.net/plain; echo. We can find mac address (physical address) of a computer using the command ‘getmac‘. This can be used to get mac address for remote computers also. Below are few examples on how to use this command. It works on XP, Vista, Windows 7, Server 2003 and Server 2008 operating systems. Get mac addresses from CMD.
What is MAC Address
MAC is abbreviated as Media Access Control. It is a unique 48 bit(6-byte) address assigned to a Network Interface. It is almost used in all the Network Devices which has network controller in it. It will always show in this form 00:07:Y7:1C:6L:03.
Find MAC Address in Linux
Also Read:25 Useful Linux SS Command Examples to Monitor Network Connections
Method 1: How to find MAC Address in Linux Using ifconfig command
If you want to check MAC Address of all the network interfaces in Linux using our traditional ifconfig command then you need to use ifconfig -a command as shown below.
NOTE:
root user to run all the below commands.You can use any user with sudo access to run all these commands. For more information Please check Step by Step: How to Add User to Sudoers to provide sudo access to User.Method 2: How to find an ethernet MAC Address in Linux Using ifconfig command
If you want to check the MAC Address of a specific network interface using ifconfig command then you need to use network interface name with ifconfig command as shown below. Here we are checking MAC Address of interface enp0s3 using ifconfig enp0s3 command.
NOTE:
eth0 network interface in your system instead of enp0s3. Hence Please use the network interface name with all the mentioned commands as per your system interface name or else none of the command will work.Method 3: How to find MAC Address in Linux Using ip addr sh command
If you want to check the MAC address of all the network interfaces then you need to simply use ip addr sh command and check the MAC address from ether field as shown below.
Method 4: How to find an ethernet MAC Address in Linux using ip addr sh command
If you want to check the MAC address of some specific network interface then you need to use the interface name with ip addr sh command and check the MAC address from ether field as shown below. In this example we are checking MAC address of enp0s3 network interface.
Method 5: How to find MAC Address in Linux Using ip link show command
If you want to check the MAC address of all the network interfaces then you can use another useful ip link show command and check the MAC address from link/ether field as shown below.
Method 6: How to find an ethernet MAC Address in Linux using ip link show command
If you want to check the MAC address of some specific network interface then you need to use the interface name with ip link show command and check the MAC address from ether field as shown below. In this example we are checking MAC address of enp0s3 network interface.
Method 7: How to find MAC Address in Linux using ethtool command
You can also use another useful linux tool called ethtool to find MAC address in Linux as shown below. Here I am checking MAC address of my ethernet card enp0s3 using ethtool command hence you need to mention your Interface name before running below command.
Method 8: How to find MAC Address in Linux using Regex with ifconfig command
You can use a simple grep regular expression with ifconfig command to find the MAC Address of an ethernet card in Linux as shown below. Like above example, Here I am using regular expression on my System enp0s3 interface so you need to change and mention your interface name instead of enp0s3 before running below command.
Method 9: How to find MAC Address in Linux using SYS Files
If you want to check MAC address in Linux using SYS files you need to check network address file using below cat command. As mentioned below SYS file is a text file so its contents can always be seen through Linux cat command.
Method 10: How to find MAC Address in Linux using AWK Regex with ifconfig command
You can also use AWK regular expression with ifconfig command to find MAC Address in Linux as shown below. Here we are grepping ether keyword from ifconfig command and then piping to awk to get first and second column output separated by tab.
Method 11: How to find MAC Address in Linux using Sed Regex with ifconfig command
Like above example, you can also use Sed Regular expressions with ifconfig command to find MAC Address in Linux as shown below.
Popular Recommendations:-
How would you communicate with a device when you don’t have the IP?
You might be in a situation where you don’t have the IP address of a device in a local network, but all you have is records of the MAC or hardware address.
Or your computer is unable to display its IP due to various reasons, and you are getting a “No Valid IP Address” error.
Finding the IP from a known MAC address should be the task of a ReverseARP application, the counterpart of ARP.
But RARP is an obsolete protocol with many disadvantages, so it was quickly replaced by other protocols like BOOTP and DHCP, which deal directly with IP addresses.
In this article, we’ll show you how to find IPs and device vendors using MAC addresses with different methods for free.
Understanding ARP
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is the protocol in charge of finding MAC addresses with IPs in local network segments.
It operates with frames on the data link layer.
As you might already know, devices in the data link layer depend on MAC addresses for their communication.
Their frames encapsulate packets that contain IP address information.
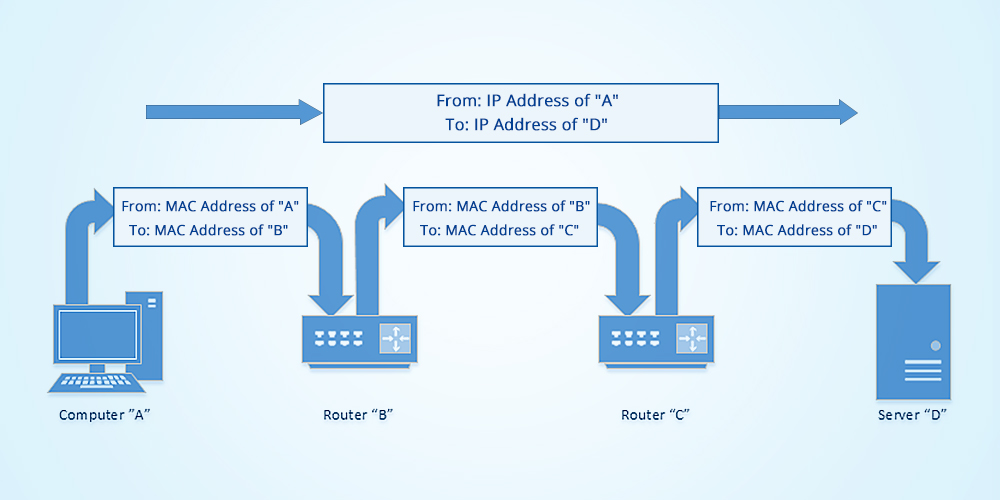
A device must know the destination MAC address to communicate locally through media types like Ethernet or Wifi, in layer 2 of the OSI model.
Understanding how ARP works can help you find IPs and MAC addresses quickly.
The following message flow diagram can help you understand the concept:
- The local computer sends a ping (ICMP echo request) to a destination IP address (remote computer) within the same segment. Unfortunately, the local computer does not know the MAC address… it only knows the IP address.
- The destination hardware address is unknown, so the ICMP echo request is put on hold. The local computer only knows its source/destination IP and its source MAC addresses. ARP uses two types of messages, ARP Request and Reply.
The local computer sends an ARP REQUEST message to find the owner of the IP address in question.
This message is sent to all devices within the same segment or LAN through a broadcast MAC (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) as the destination.
- Because the remote computer is part of the same network segment, it receives the broadcast message sent by the local computer. All other computers in the LAN also receive the broadcast but they know that the destination IP is not theirs, so they discard the packet. Only the remote computer with destination IP, responds to the ARP REQUEST with an ARP REPLY, which contains the target MAC address.
- The local computer receives the ARP REPLY with the MAC address. It then resumes the ICMP echo request, and finally, the remote computer responds with an ICMP echo reply.
Finding IPs with ARP
You can use ARP to obtain an IP from a known MAC address.
But first, it is important to update your local ARP table in order to get information from all devices in the network.
Send a ping (ICMP echo reply) to the entire LAN, to get all the MAC entries on the table.
To ping the entire LAN, you can send a broadcast to your network.
Open the Command Prompt in Windows or terminal in macOS and type.
ping 192.168.0.255
My subnet is 192.168.0.0/24 (mask of 255.255.255.0), so the broadcast address is 192.168.0.255 which can be calculated or found with a “Print Route” command in Windows or a “netstat -nr” in macOS. Or can also be obtained with a subnet calculator.
For Windows:
Step 1.

- Open the CMD (Command Prompt)
- Go to the “Start” menu and select “Run” or press (Windows key + R) to open the Run application
- In the “Open” textbox type “cmd” and press “Ok”.
This will open the command-line interface in Windows.
Step 2.
Finding Mac Address From Ip Address On Network
- Enter the “arp” command.
- The arp command without any additional arguments will give you a list of options that you can use.
Step 3.
- Use the arp with additional arguments to find the IP within the same network segment.
- With the command “arp -a” you can see the ARP table and its entries recently populated by your computer with the broadcast ping.
Step 4.
- Reading the output.
- The information displayed in the arp-a is basically the ARP table on your computer.
- It shows a list with IP addresses, their corresponding physical address (or MAC), and the type of allocation (dynamic or static).
Let’s say you have the MAC address 60-30-d4-76-b8-c8 (which is a macOS device) and you want to know the IP.
From the results shown above, you can map the MAC address to the IP address in the same line.
The IP Address is 192.168.0.102 (which is in the same network segment) belongs to 60-30-d4-76-b8-c8.
You can forget about those 224.0.0.x and 239.0.0.x addresses, as they are multicast IPs.
For macOS:
Step 1:
- Open the Terminal App. go to Applications > Utilities > Terminal or Launchpad > Other > Terminal.
Step 2:
- Enter the “arp” command with an “-a” flag.
- Once you enter the command “arp -a” you’ll receive a list with all ARP entries to the ARP Table in your computer.
- The output will show a line with the IP address followed by the MAC address, the interface, and the allocation type (dynamic/static).
Finding IPs with the DHCP Server
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is the network protocol used by TCP/IP to dynamically allocate IP addresses and other characteristics to devices in a network.
The DHCP works with a client/server mode.
The DHCP server is the device in charge of assigning IP addresses in a network, and the client is usually your computer.
For home networks or LANs, the DHCP Server is typically a router or gateway.
If you have access to the DHCP Server, you can view all relationships with IPs, MACs, interfaces, name of the device, and lease time in your LAN.
Step 1.
- Log into the DHCP Server. In this example, the DHCP server is the home gateway.
- If you don’t know the IP address of your DHCP Server/ Gateway, you can run an ipconfig (in Windows) or ifconfig (in macOS/Linux).
- This particular DHCP Server/Gateway has a web interface.
Step 2.
- Enter the IP address on the search bar of the web browser, and input the right credentials.
Step 3.
- Find the DHCP Clients List.
- In this TP-Link router, the DHCP Server functionality comes as an additional feature.
- Go to DHCP > DHCP Clients List. From this list, you can see the mapping between MAC addresses and their assigned IPs.
Using Sniffers
If you couldn’t find the IP in the ARP list or unfortunately don’t have access to the DHCP Server, as a last resort, you can use a sniffer.
Packet sniffers or network analyzers like Nmap (or Zenmap which is the GUI version) are designed for network security.
They can help identify attacks and vulnerabilities in the network.
With Nmap, you can actively scan your entire network and find IPs, ports, protocols, MACs, etc.
If you are trying to find the IP from a known MAC with a sniffer like Nmap, look for the MAC address within the scan results.
How to find the Device and IP with a Sniffer?
Step 1.

- Keep records of your network IP address information.
- In this case, my network IP is 192.168.0.0/24. If you don’t know it, a quick “ipconfig” in Windows cmd or an “ifconfig” in macOS or Linux terminal can show you the local IP and mask.
- If you can’t subnet, go online to a subnet calculator and find your network IP.
Step 2.
- Download and open Nmap.
- Download Nmap from this official link https://nmap.org/download.html and follow its straightforward installation process.
Step 3.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001_find-a-mac-address-using-an-ip-address-818132-5c6f241246e0fb00014361c5.jpg)
- Open Nmap (or Zenmap) and use the command “sudo nmap -sn (network IP)” to scan the entire network (without port scan).
- The command will list machines that respond to the Ping and will include their MAC address along with the vendor.
- Don’t forget the “sudo” command.
- Without it, you will not see MAC addresses.
Finding out the device vendor from a MAC address
Ok, so now you were able to find out the IP address using “arp -a” command or through the DHCP Server.
But what if you want to know more details about that particular device?
What vendor is it?
Your network segment or LAN might be full of different devices, from computers, firewalls, routers, mobiles, printers, TVs, etc.
And MAC addresses contain key information for knowing more details about each network device.
Show Mac Address For Ip Address Subnet
First, it is essential to understand the format of the MAC address.
Traditional MAC addresses are 48 bits represented in 12-digit hexadecimal numbers (or six octets).
The first half of the six octets represent the Organizational Unique Identifier (OUI) and the other half is the Network Interface Controller (NIC) which is unique for every device in the world.
There is not much we can do about the NIC, other than communicating with it.
But the OUI can give us useful information about the vendor if you didn’t use Nmap, which can also give you the hardware vendor.
A free online OUI lookup tool like Wireshark OUI Lookup can help you with this.
Just enter the MAC address on the OUI search, and the tool will look at the first three octets and correlate with its manufacturing database.
Final Words
Although the RARP (the counterpart of ARP) was specifically designed to find IPs from MAC addresses, it was quickly discontinued because it had many drawbacks.
RARP was quickly replaced by DHCP and BOOTP.
But ARP is still one of the core functions of the IP layer in the TCP/IP protocol stack.

It finds MAC addresses from known IPs, which is most common in today’s communications.
ARP works under the hood to keep a frequently used list of MACs and IPs.
But you can also use it to see the current mappings with the command arp -a.
Aside from ARP, you can also use DHCP to view IP information. DHCP Servers are usually in charge of IP assignments.
If you have access to the DHCP server, go into the DHCP Client list and identify the IP with the MAC address.
Finally, you can use a network sniffer like Nmap, scan your entire network, and find IPs, and MACs.
If you only want to know the vendor, an online OUI lookup like Wireshark can help you find it quickly.
